GoodApple Nutritionals
Bloat Buster
Bloat Buster
5.0 / 5.0
(3) 3 total reviews
Couldn't load pickup availability
Provides quick relief from gas and bloating and supports digestion of fats.
If you find yourself eating a fatty meal and then feeling regrets, Bloat Buster is your new best friend!
Bloat Buster's key features:
Relieves gas and bloating
For those with gallbladder or no gallbladder
Supports bile flow
Contains bile salts
Supports gallbladder and liver
Bile salts and choline support fat digestion
Feeling uncomfortable and bloated? Bloat Buster is here to help! Our all-natural formula works quickly to support your digestive health so you can feel lighter and more energized in no time.
Whether it's from a big meal or just everyday discomfort, Bloat Buster provides the relief you need to get back to your day with confidence.
Natural ingredients aid in breaking down food for smoother digestion
Safe & gentle, non-habit-forming and suitable for daily use
Convenient and easy to use, simply take the recommended dose and quickly feel the difference
Order Bloat Buster today and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable you!
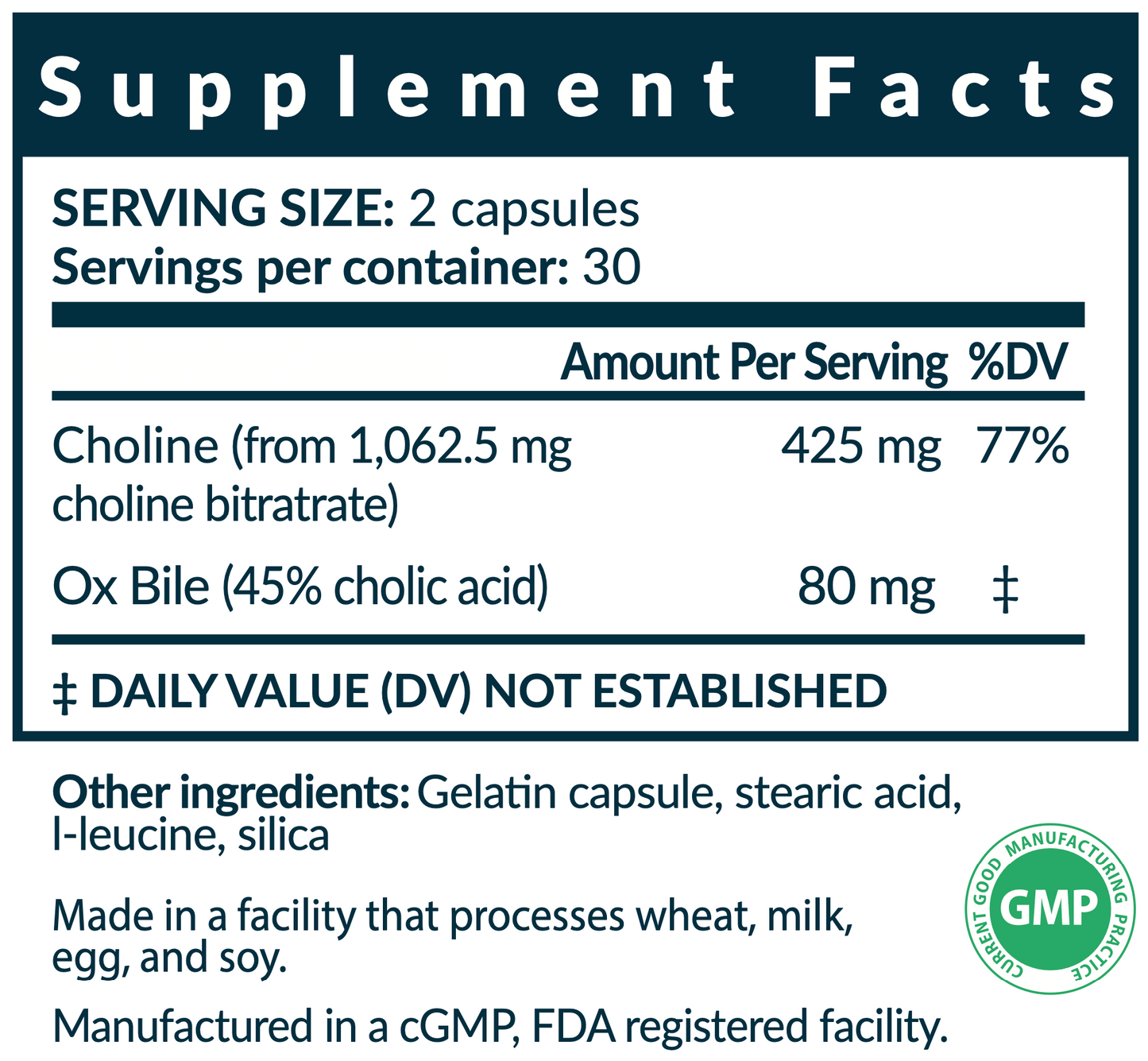
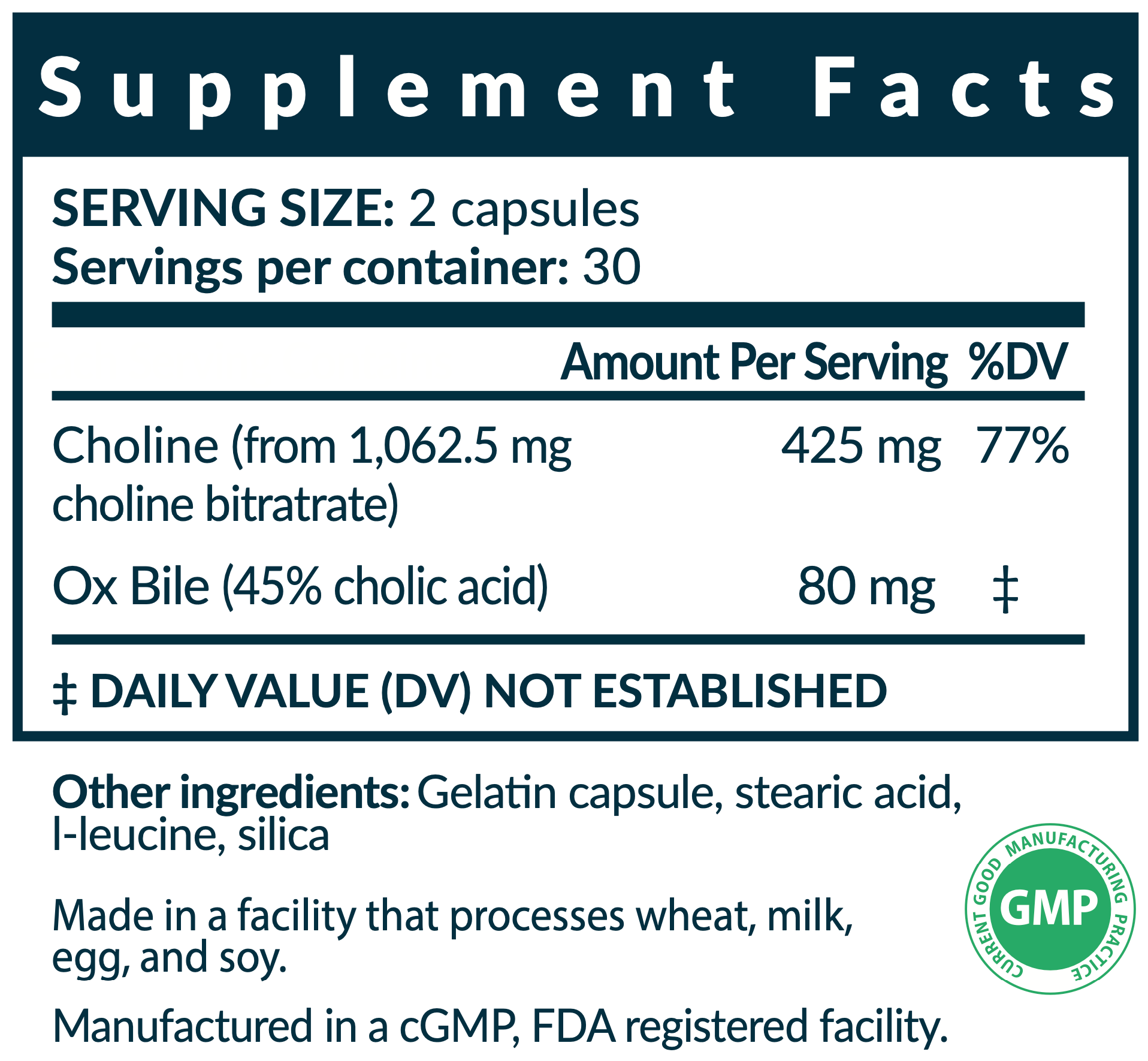
Dosage: Take 2 capsules just before meals.
Bloat Buster contains ox bile, choline, and l-leucine.
The Benefits of Ox Bile
Ox bile may help reduce gas and bloating through its effects on fat digestion and absorption. Here are three ways ox bile might be helpful:
Improved Fat Digestion
One of the primary roles of bile salts is to aid in the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. By supplementing with ox bile, individuals with inadequate bile production or compromised gallbladder function might improve their ability to digest fats more efficiently. Undigested fats in the gut can contribute to bloating and gas, so better fat digestion may help alleviate these symptoms.
Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
Proper fat digestion facilitated by bile salts can also lead to better absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and other essential nutrients. Adequate absorption of nutrients is essential for overall digestive health and may reduce symptoms of gas and bloating associated with nutrient malabsorption.
Balanced Gut Microbiome
Some studies suggest that bile acids, including those found in ox bile, may play a role in modulating the gut microbiome. A healthy and balanced gut microbiome is crucial for efficient digestion and can contribute to reducing gas and bloating.
The Benefits of Choline
Supports Liver Function
Choline is a precursor to phosphatidylcholine, a vital component of cell membranes and lipoproteins. Adequate choline levels help maintain liver health and function, as it supports the transport of lipids from the liver to other tissues.
Supports Fat Metabolism & Transport
Choline aids in the transport of lipids from the liver to other tissues and supports the removal of excess fat from the liver, which is crucial for maintaining liver health. A well-functioning liver is crucial for proper fat metabolism, which may help reduce the risk of excessive gas and bloating caused by undigested fats.
Supports Nervous System Regulation
Choline is a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in various functions, including gut motility and digestion. Proper nervous system regulation is essential for coordinating the movement of food through the digestive tract. A study in The Journal of Nutrition highlights the importance of choline in brain development and neurotransmitter synthesis. By supporting the production of acetylcholine, choline might indirectly help regulate gut motility and reduce the risk of gas and bloating caused by poor digestion.
The Benefits of L-leucine
Gut Barrier Integrity
Some studies suggest that amino acids, including L-leucine, can play a role in supporting gut barrier integrity. A healthy gut barrier is essential for preventing the passage of harmful substances from the gut into the bloodstream and for maintaining gut health. A review in the journal Nutrients discusses the role of amino acids in supporting gut barrier function.
Modulation of Gut Hormones
Some research suggests that certain amino acids, including L-leucine, can influence gut hormone secretion, such as cholecystokinin (CCK) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). These hormones play roles in regulating appetite, digestion, and nutrient absorption. A recent study found that dietary L-leucine intake led to increased GLP-1 secretion, which may impact digestion and nutrient absorption while increasing insulin sensitivity and the sensation of satiety.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation in the gut can lead to various digestive issues. Some studies suggest that amino acids such as L-leucine may have anti-inflammatory properties. A recent study demonstrated that a diet enriched with essential amino acids, including L-leucine, reduced markers of inflammation in the colon.
Share